Off-grid solar power systems are designed to provide electricity in locations that are not connected to the traditional power grid. These systems typically consist of several components:
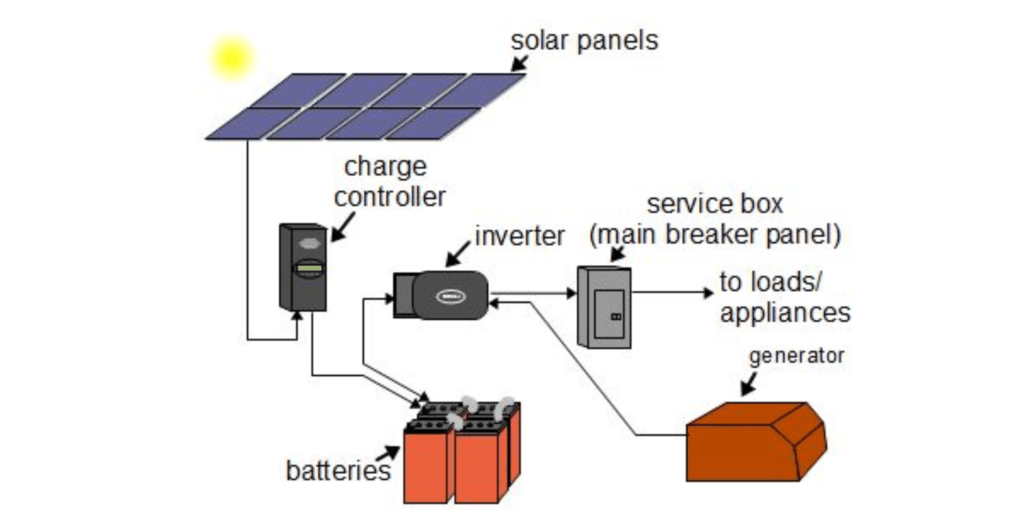
- Solar Panels: These devices capture sunlight and convert it into electricity through the photovoltaic effect. The panels are usually mounted on rooftops or ground-mounted arrays to maximize solar exposure.
- Charge Controller: A charge controller regulates the amount of electricity flowing from the solar panels to the batteries. It prevents overcharging and extends the battery lifespan.
- Batteries: The energy generated by the solar panels is stored in batteries for later use, especially during periods of low sunlight or at night. Common battery types used in off-grid systems include lead-acid, lithium-ion, and deep-cycle batteries.
- Inverter: Since most off-grid solar power systems generate DC (direct current) electricity, an inverter is required to convert it into AC (alternating current) electricity, which is used by most household appliances and devices.
- Generator (Optional): In some cases, a backup generator may be incorporated into the system to provide additional power during extended periods of low sunlight or increased electricity demand.
- Electrical Wiring and Breakers: The system requires appropriate electrical wiring and circuit breakers to distribute electricity from the solar panels, batteries, and inverter to various loads within the property.
- Monitoring System: Some off-grid systems include a monitoring system that provides real-time information on the performance and status of the system, including battery charge level and energy consumption.